3.3. DELETE
DELETE statement is used to delete a single record or multiple records from a table in SQL Server.
QUERY :- DELETE FROM tbname WHERE condition ;
EXAMPLE :- DELETE FROM employee WHERE e_id = 1;
Also you can write two condition at a time. For that you will use AND, OR, NOT operators.
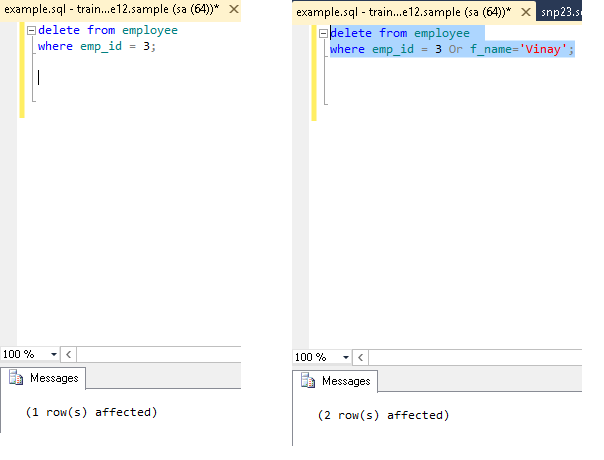
EXAMPLE :- DELETE FROM employee
WHERE e_id = 1 AND f_name=’Vinay’;
NOTE: - if you execute only
DELETE FROM employee;
This statement is delete all data from the table.
Difference between DELETE and TRUNCATE.
DELETE
TRUNCATE
It is a DML command
It is a DDL command
The command is used by using row lock operation
The command is used and executed with table lock operation to remove all the records
To filter any specific row or data we can use WHERE clause
We cannot use WHERE clause with this command
A log is maintained in this command so is a slower command
No log is maintained so is comparatively faster
Rows are removed on eating a time in this command and for each delete operation a transaction log entry is being done
It removes the data by deallocating the pages that are used to store data and only records the pages that are deallocated in the transaction log.
DELETE operation retain the table identity
The column is reset to the seed value if any identity column is there in the table
You need DELETE permission for the table to use this operation
You need DELETE permission for the table to use this operation
It uses more transaction space than TRUNCATE operation
It uses less transaction space than DELETE operation
It can be used with indexed views
It cannot be used with indexed views
