Basic Transducers
Definition and General Concept of Transducer
Definition
The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form.
Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer
Electrical Transducer: A device which converts a physical quantity into the proportional electrical signal is
called electrical transducer.
Advantages of Electrical Transducer:
- Electrical output can be amplified to any desired level
- Low power requirement
- Easy transmission
- Suitable with digital control
- Low cost
- Small size
- Reduced friction effect
- The output can be modified as per requirements of the indicating or controlling equipments
Characteristics of Transducer:
- High accuracy
- Rugged
- High output
- High stability and reliability
- High sensitivity
- Small size
- Fast speed of response
- Dynamic range
- Possess repeatability
Selection factor of Transducers:
- Nature of measurement
- Range
- Loading effect
- Environmental considerations
- Measuring system compatibility
- Cost and availability
- Errors
- Calibration
Classification of Transducers
The following is the basic classification of the transducers. The figure 5.1 shows the classification of transducers. Active Transducer The transducers, which develop their output in form of electrical voltage or current without any auxiliary source are known as active transducers. They draw energy from the system under measurement. They give very small output and use of amplifier is essential. Examples: Tachogenerator, Thermocouple, Piezo-electric crystals, photovoltaic cell etc. The transducers in which, the electrical parameters i.e. resistance, inductance and capacitance changes with change in input signal. They require external power source for energy conversion. In this, electrical parameters causes a change in voltage, current or frequency of the external power source. They may draw some energy from the system under measurement. Examples: Resistive, Inductive and Capacitive transducers Analog transducer converts input signal into output signal, which is a continuous function of time. Examples: Thermistor, Strain gauge, LVDT, Thermocouple Digital transducer converts input signal into output signal of the form of pulses e.g. it gives discrete output. These transducers are becoming more popular. Sometimes, analog transducer combined with ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) is called digital transducer. Examples: Encoders, Hall effect sensors When input signal is directly sensed by transducer and physical phenomenon is converted into electrical form directly then such transducer called primary transducer. Examples: Thermistor When input signal is directly sensed first by some sensor and then its output being of some form other than input signal I given as input to a transducer for conversion into electrical form, then it’s called secondary transducer. Examples: LVDT for used pressure measurement by using bourdon tube It is a device that converts a non-electrical quantity into an electrical quantity. Examples: Thermocouple, Pressure gauge, Strain gauge, Photovoltaic cell It is a device that converts an electrical quantity into non-electrical quantity. It is a precision actuator having an electrical input and low-power non-electrical output. A most useful application of inverse transducer is in feedback measurement systems. Examples: Piezo-electric crystal A device which converts linear or angular motion into electrical output signal is known as displacement transducer. Examples: LVDT, RVDT, Gyroscope A device which converts pressure or force into electrical output signal is known as pressure or force transducer. Examples: Strain gauge, Piezo-electric transducer, Bourdon tube transducer A device which converts transducer into electrical output signal is known as pressure or force transducer. Examples: Thermocouple, Thermistor, RTD A device which converts flow into electrical output signal is known as pressure or force transducer. Examples: Ultrasonic flowmeter, Hotwire anemometer A transducer which works on the resistive principle is known as resistive transducer. Examples: Potentiometer, Strain gauge, RTD, Thermistor, Hotwire anemometer A transducer which works on the inductive principle is known as resistive transducer. Examples: LVDT, RVDT, Synchro A transducer which works on the capacitive principle is known as resistive transducer. Examples: Capacitor microphone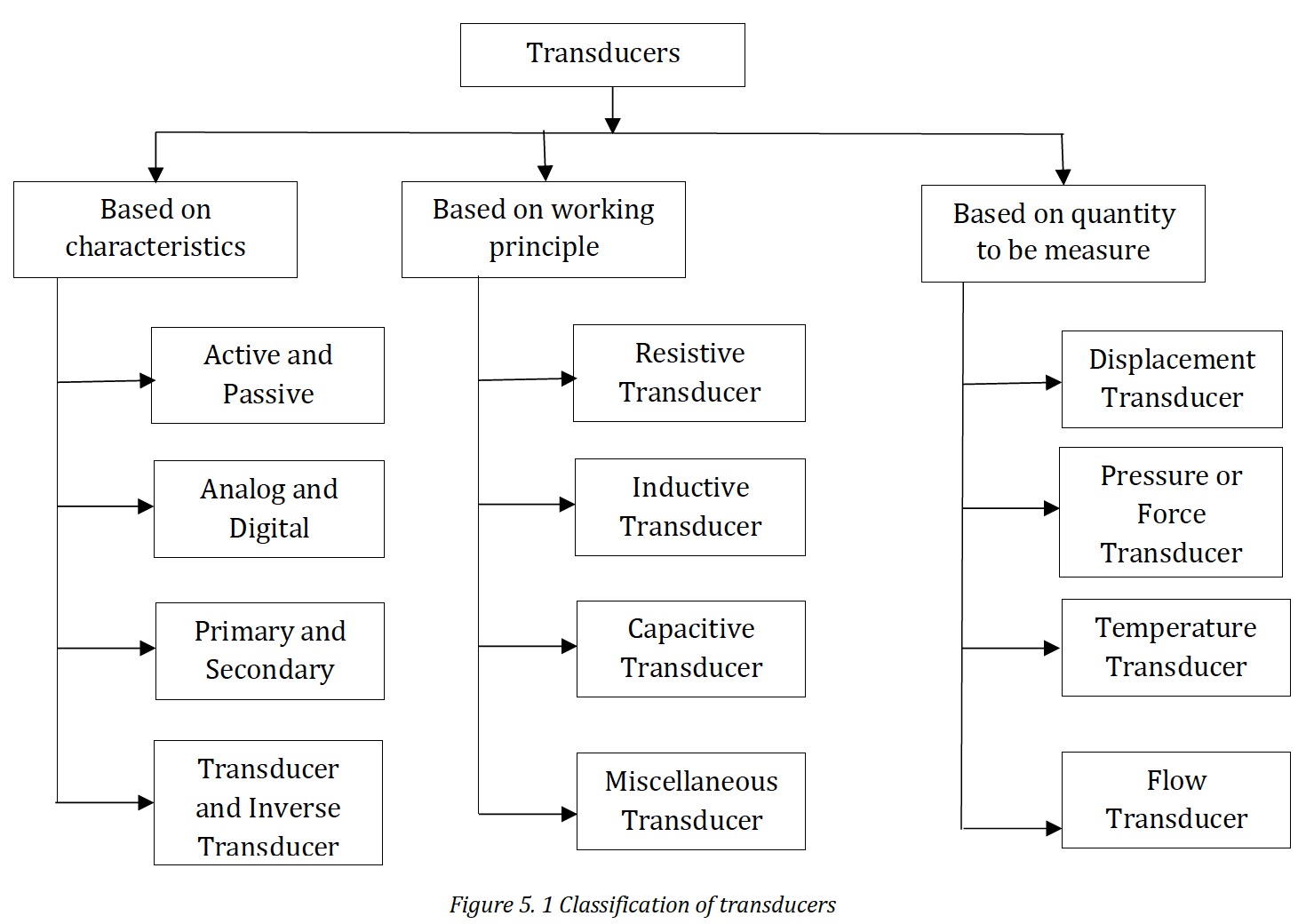
Passive Transducer
Analog Transducer
Digital Transducer
Primary Transducer
Secondary Transducer
Transducer (Electrical)
Inverse Transducer
Displacement Transducer
Pressure or Force Transducer
Temperature Transducer
Flow Transducer
Resistive Transducer
Inductive Transducer
Capacitive Transducer
